Everything Evolution
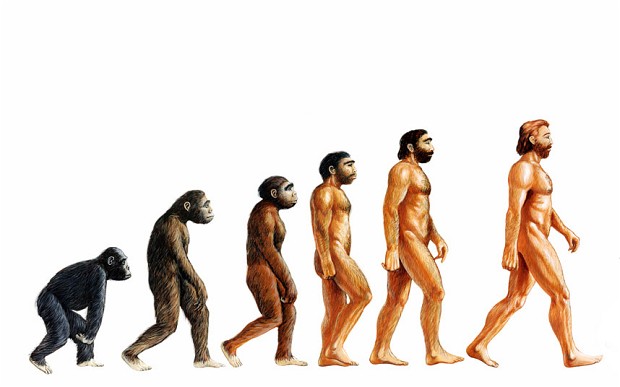
We have all heard of the theory of evolution, or at least something involved with the word evolution. Some things you might associate with this word is Charles Darwin (the founder), science vs. Christians, or the origin of life. Truth be told, none of this is 100% true. So, with so many misconceptions, what is evolution exactly? As we have discussed in class, the very simple description of the evolution theory is change over time. Or, the google definition quotes exactly, “The gradual development of something, especially from a simple to a more complex form.” Evolution is a mess of many components. But, first, to understand the concept of evolution, you have to understand the many minds that were behind the idea.
Like the common misconception, the main person we would associate with evolution is Charles Darwin. Though, before there was Darwin, there were a great deal of others first. To begin, there was Erasmus Darwin (1731-1802), the grandfather of Charles Darwin. A respected physician, poet, philosopher, botanist, and naturalist. He had one of the first theories of evolution. He believed that life evolved from a single common ancestor. His theory stated that the change in species occurred from competition and sexual selection. You could call this phenomenon natural selection.
Jean Baptiste Lamarck (1744-1829) was an early evolutionist whose ideas were never accepted. Actually, they were most often laughed at. Upon his death, Lamarck died in poverty and in obscurity. At the National Museum of Natural History, he was professor of invertebrates- not the most appreciated field. In his studies, he created the theory that organisms changed based on their environmental needs and changes. He theorized that species’ organs and structures shrink or disappear depending on their needs in the environment. Every organism started out simple and slowly becomes more complex to strive towards perfection.
George Cuvier (1769-1832) went to a school founded by the French Duke. He later then became a naturalist and professor in animal anatomy. A lot of his research came from that in his study of fossils. He did not believe in organic evolution. In his mind, everything happened and was created for a reason. Fossils he found and studied weren’t much different than that of those known in the present time. Like that of a mummified cat. The cat fossil was the same of that in present day. This lead him to believe that past catastrophic events had wiped away some creatures and new ones were placed on the Earth to make up for those lost. His research lead him to believe in similarities in fossils ment that the past creatures had the same functions. That was his idea of evolution. Creatures becoming different but staying the same creature over time.
Last, but certainly not least, there is the well known Charles Darwin (1809-1882). Charles Darwin was a naturalist with an amazing opportunity. Along boarding the HMS Beagle, he was given the opportunity to travel and observe the world for five years, a very rare thing during his day and age. During his voyage, he suffered awful sea sickness to have his ship stumbled upon the Galapagos Islands, the most prominent destination of his evolution discoveries. He collected and observed many specimens of birds, plants, animals, and fossils. Many of the creatures he observed on the isolated island were similar to those around the world. This gave notation a common ancestor. There was one main way that the species had been surviving. Natural selection. Those species who were able to withstand the challenges of environment and reproduce lived and prospered. One example was his study of the finches on the Galapagos Islands. Although he did not understand or realize it until he was back in London, Darwin studied 13 types of finches on the Galapagos Islands, each coming from a different island. The thought brought him to the understanding that each finch had derived from a common ancestor, but had to use the process of natural selection to adapt and survive on their new environment. Evolutions could spur from the diet of the finches to the geological area. Darwin’s research opened up a whole new standpoint on the theory of evolution. There became a couple of different subjects to study on the subject.
Microevolution is the evolutionary change of species over a shorter period of time between populations. Populations are species from the same gene pool that breed with one another. This form of evolution includes the idea of natural selection. There are four different studied typed of microevolution:
- Natural selection, or the ability of species to adapt to the dangers of their environment to work towards the goal of reproducing and surviving.
- Mutation. Also known as new changing in your DNA.
- Migration, which can happen when different populations come in contact and breed with another population. This can happen from immigration or emigration.
- Lastly, genetic drift, where we see certain genes becoming more frequent and overriding other genes.
In our observed nature, we have seen microevolution happen with bacteria’s that are normally harmful in our bodies learn to resist antibiotics. When the antibiotic kills most, but not all, of a bacteria, the bacteria is likely to return to it’s normal size. Eventually, this will result in a strain of bacteria that is antibiotic resistant. This is because the bacteria had changed in gene and allele frequencies to survive against the antibiotic.
Next on the subtypes of evolution, we have macroevolution. This is the complete opposite of microevolution. It is the major change of groups over a long period of time. How do we know that this has occurred though? One way that we for sure know is through the fossil record. For example, it is thought that birds descended from dinosaurs. They have similar skeletal structures, some dinosaurs had wings, and some even had feathers! Based on the skeletal structures of bipedal, flying dinosaur fossils observed by archeologists, it is an understandable statement to say that especially the species of our beloved turkey’s is a descended form of an evolved dinosaur. Also, in many fossils, we can identify and group their feature to a certain class. Each class came from a previous period of time, or Epoch. For humans, there are six classes that we can group our evolved fossil forms into today. Order, suborder, infraorder, hominoid, hominid, or homo. Features and adaptations can give clue to when a fossil might have been living in or evolved from. We can call this identification comparative morphology, or locating similar bodily structures and plans of an organism.
But, is just the fossil records enough in the world of macroevolution? Of course not. There is also the evidence in the two scientific fields of study, biochemistry and embryology. Embryology focuses on the unborn specimen of a species and how species are alike in the embryo. Take, for example, us humans and fish. In the embryo, we both have gills. But, why do the gills on humans disappear before birth? Probably, because we don’t live in water, while fish do. Our environment above water has evolved so that we don’t keep that unnecessary trait. Does this mean that humans were either fish or lived underwater at some point? No. Just that we have a common ancestor. But, overtime, our certain species evolved to fit our needs. Biochemistry is a little bit different. It focuses more on our chemical makeup, or our DNA. The biochemistry of our cells strongly show a common ancestor in some organisms. Proteins can support this theory strongly. Plenty of protein structures are similar or the same as other species, giving hint to a common ancestor. Take the beta globin protein in us humans and chimps for example. There is a 99% similarity. With that fact, it is hard to not believe that there’s the possibility we derived from a common ancestor. The beta globin protein is not the only similar protein. There are hundreds, even thousands, of similar amino sequences in the world of organisms. Biochemistry studies and records all these DNA similarities to support this evolution theory.
Like stated above, evolution is just a theory. It is something that you should neither believe in or put your faith into. Though, still, these days we hear many arguments about whether or not evolution is real or not real. Most don’t realize that evolution isn’t 100% proved yet and it can only be proved by scientific facts. What science can do is convince us using proof that evolution of past species have actually changed over time. So, did all of this information convince me?
To be honest, at the beginning of this essay, I was slightly skeptical about evolution. I really didn’t even understand what it was. But, after my rigorous research, I think that I do infact believe that species have changed over time. Some things that convince me are from events that are happening today.
One example today is definitely with bacteria/viruses and antibiotics. As bacteria and viruses adapt to your immune system and current antibiotics, they start to over power and evolve into a bacteria or virus that can withstand the conditions being acted upon it. It changes so it can prosper. This is why the people who make our drugs have to stay ahead of the antibiotics game. There are actually many antibiotics that have not be released to us. Why? As soon as they are in our immune systems and present to us the quicker that the viruses can evolve to survive the conditions of the antibiotic. Also, this is why antibiotics, such as Penicillin, can be so harmful. Viruses in your body have evolved to withstand the antibiotic. Instead, the antibiotic causes an allergic reaction, such as hives. The allergic reaction continues to worsen and worsen the more the evolved virus comes in contact with the antibiotic. Eventually, a human’s body will go into anaphylactic shock and you will die instantly. This worry affects me personally due to the fact that I am allergic to Penicillin. Let’s say, for instance, I get an ear infection. Taking the antibiotic Penicillin is not an option for me because the virus in my body has already evolved to overcome the medicine. I would have to take a new antibiotic that has not yet evolved.
Another example is that of moths. The Peppered Moths, to be specific, in England. The light colored ones use to blend in perfectly to trees with white tree trunks. This helped them to not get eaten by predators. But, during the industrial revolution, all the smoke and the ash caused the white trees to turn a dark black color and all the moths were exposed. The moth population started to decrease. But, then something happened. The population stopped decreasing because they were less exposed to their predators. How? By the process of many mutations and natural selection, the moths began to darken in color. The moths had already had the darker traits inside them, but did not expose them because it wasn’t necessary for their survival. With natural selection, the moths breed with other moths that could expose the dark color. It took several reproductions, but the moths were able to evolve and blend in again to the trees for survival.

Based on these facts, the information I have learned, and the exact definition, I believe that evolution is a believable theory that is most definitely proved by scientific fact. Before, I couldn’t actually tell you anything about evolution. But, now I can give you hard evidence facts and descriptions to support the theory. I guess, now my question is, can you?
Below is my list of resources:
http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/history/evothought.html
http://whyfiles.org/125galapagos/index.html
http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/library/index.html
http://www.biography.com/people/charles-darwin-9266433
http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/evo_36
http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Microevolution
http://www.agiweb.org/news/evolution/examplesofevolution.html
http://necsi.edu/projects/evolution/evidence/embryos/evidence_embryo.html
https://www.ministrymagazine.org/archive/1973/11/biochemistry-and-the-study-of-evolution